Partnering with patients, carers, and the broader community, collectively referred to as consumers, is fundamental to achieving meaningful and sustainable improvements in healthcare. Their insights, shaped by lived experience and direct interaction with health services, enhance the relevance and impact of healthcare initiatives.
This approach aligns with the National Safety and Quality Health Service Standards, developed by the Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care to protect the public and improve care quality. In particular, Standard 2: Partnering with Consumers, highlights the importance of involving consumers in the design, delivery, and evaluation of care, to ensure services are person-centred and responsive.
Our research confirms the value of consumer partnerships but also reveals that the barriers and enablers to effective involvement vary between healthcare improvement and research contexts. These differences call for tailored strategies that reflect the distinct goals and frameworks of each setting.
We also identified the need for more nuanced approaches to consumer and community involvement. While healthcare improvement falls under a safety and quality framework, research is governed by the National Health and Medical Research Council, leading to varied understandings and applications of consumer and community involvement.
Looking ahead, we will develop practical resources to support healthcare professionals in embedding consumer partnerships into improvement initiatives, ensuring these efforts are evidence-informed, person-centred, and equitable. In the interim, we’re pleased to offer a selection of foundational resources via the Health Research Hub, including case studies, frameworks, and tools to support early engagement and build capacity.
Numerous guidelines and statements highlight a range of closely aligned values and principles that form the foundation of consumer and community involvement. The Department of Health and Aged Care, National Consumer Engagement Strategy for Health and Wellbeing, provides Good Practice Guidelines to guide policy makers, health service providers and community organisations. Consumer engagement fundamentals provide a foundational framework for meaningful and effective engagement between policy-makers and consumers.
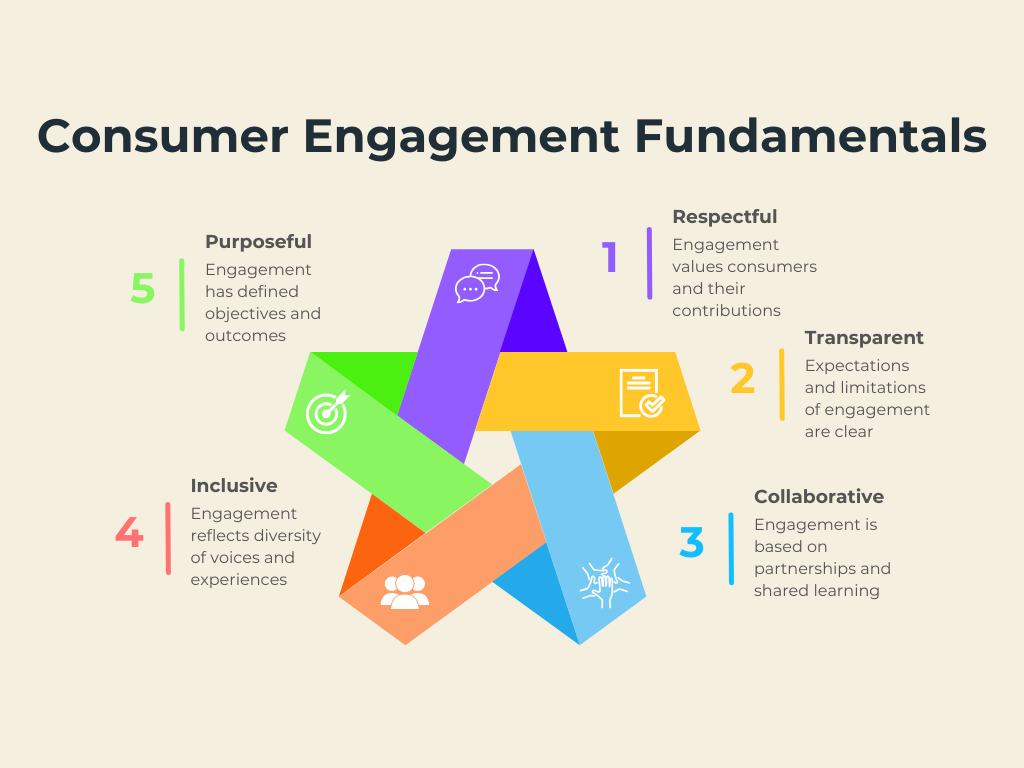
These principles are supported by Good Practice Guidelines that offer practical steps for implementing consumer engagement, including building relationships, understanding context, adapting methods, and evaluating impact:
- Build and sustain relational, not transactional partnerships.
- Develop a detailed understanding of the context.
- Identify who to engage.
- Seek and support diverse engagement participation.
- Meet people where they are.
- Understand that people require different approaches.
- Engage with humility and empathy.
- Don’t let ‘perfect’ be the enemy of good.
- Seek and act on feedback.
- Monitor engagement and evaluate impact.
For more information, including implementation guidance, please refer to the document below.
Please see additional resources that highlight the values and principles that underpin good practice in consumer and community involvement.